All Posts
Red Hat OpenStack Platform 16.1
We are testing OCS on OCP on OSP, this installation is described in three parts:
- Part 1: Red Hat OpenStack Platform 16.1 installation
- Part 2: OpenShift Container Platform 4.6 installation
- Part 3: OpenShift Container Storage 4.5 installation
Let’s first deploy Red Hat OpenStack Platform 16.1.
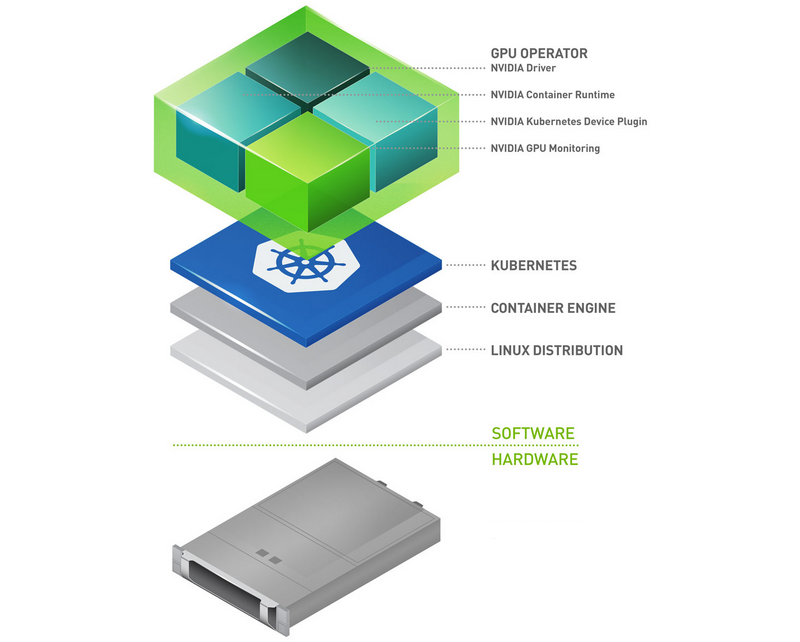
NVIDIA GPU Operator with OpenShift 4.3 on Red Hat OpenStack Platform 13
The NVIDIA GPU Operator has been available as a Beta since 2020, Jan 27, it’s a technical preview release: https://github.com/NVIDIA/gpu-operator/release
The GPU Operator manages NVIDIA GPU resources in an OpenShift cluster and automates tasks related to bootstrapping GPU nodes. Since the GPU is a special resource in the cluster, it requires a few components to be installed before application workloads can be deployed onto the GPU, these components include:
Red Hat OpenStack Platform 15 standalone
If you need to deploy quickly a testing Red Hat Openstack Platform environment, you can use standalone deployment available since Red Hat OpenStack Platform 14.
OpenShift 4.2 on Red Hat OpenStack Platform 13 + GPU
Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform 4.2 introduces the general availability of full-stack automated deployments on OpenStack. With OpenShift 4.2, containers can be managed across multiple public and private clouds, including OpenStack. Red Hat and NVIDIA are working to provide the best platform for Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning workloads.
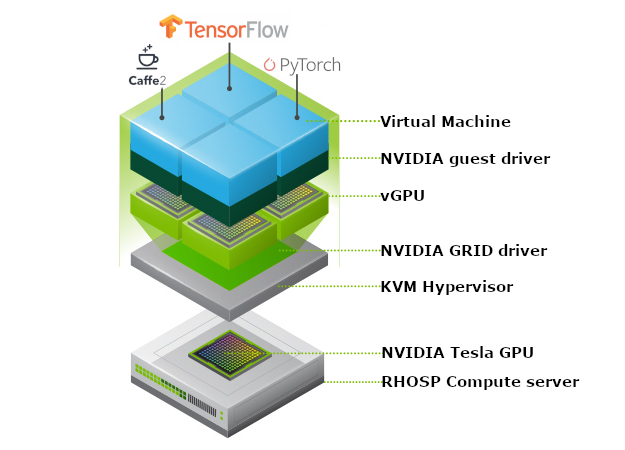
NVIDIA vGPU software and license server with RHOSP 15
We will describe the steps to try and download NVIDIA GRID software:
- Create a NVIDIA account
- Redeem your Product Activation Key (PAK)
- Download packages
- Prepare the VM and operating system of the license server based on RHEL 7.7
- Download the Virtual GPU license Manager for Linux
- Install the NVIDIA vGPU license Server
- Registering the License Server and Getting License Files
- Import the License Server file
- Launch an instance on a RHOSP 15 platform
- Instance status
- Compute node status
- Check the license status with CLI
- Check the license status in the dashboard
To enable NVIDIA GRID for Red Hat OpenStack Platform, you will need (example for RHOSP 8):\
NVIDIA vGPU with Red Hat OpenStack Platform 14
Red Hat OpenStack Platform 14 is now generally available \o/
NVIDIA GRID capabilities are available as a technology preview to support NVIDIA Virtual GPU (vGPU). Multiple OpenStack instances virtual machines can have simultaneous, direct access to a single physical GPU. vGPU configuration is fully automated via Red Hat OpenStack Platform director.
NVIDIA Tesla GPU PCI passthrough with Red Hat OpenStack Platform 13
Red Hat OpenStack Platform provides two ways to use NVIDIA Tesla GPU accelerators with virtual instances:
- GPU PCI passthrough (only one physical GPU per instance)
- vGPU GRID (one physical GPU can be shared to multiple instances, Tech Preview OSP14)
This blog post is intended to show how to setup GPU PCI passthrough.
USB Passthrough with Red Hat OpenStack Platform 13
Some OpenStack users users would like to attach USB devices to OpenStack instances for security or legacy applications.
For example, a security application which run inside an OpenStack instance could require access to a Java card from an USB Gemalto eToken: