All Posts
Unlock the Power of Mistral AI with Red Hat OpenShift AI and NVIDIA DGX H100
I will guide you through the process of deploying Red Hat OpenShift AI on the NVIDIA DGX H100 system and run the Mistral AI model. This blog post details the process of deploying and managing a fully automated MLOps solution for a large language model (LLM) presented in three main parts:
How to install Fedora and MicroShift on the NVIDIA Jetson AGX Xavier
On Dec 6, 2021, NVIDIA released the new UEFI/ACPI Experimental Firmware 1.1.2 for Jetson AGX Xavier and Jetson Xavier NX.
In this blog post, I will:
OpenShift Bare Metal provisioning with NVIDIA GPU
TL;DR
The bare metal installation of OCP is only this installer command:
$ openshift-baremetal-install --dir ~/clusterconfigs create cluster
but I’ll take time in this post to explain how to prepare your platform and how to follow the installation.
Red Hat OpenStack Platform 16.1
We are testing OCS on OCP on OSP, this installation is described in three parts:
- Part 1: Red Hat OpenStack Platform 16.1 installation
- Part 2: OpenShift Container Platform 4.6 installation
- Part 3: OpenShift Container Storage 4.5 installation
Let’s first deploy Red Hat OpenStack Platform 16.1.
CodeReady Containers with GPU for Data Science
Lots of Data Scientists want to focus on model building.
Just using a local Jupyter Notebook can be a limitation if you want to:
- create scalable Machine Learning systems
- test local private data ingestion
- contribute to Kubeflow
- tune your model serving pipeline
You can build an All-in-One Kubernetes environment with NVIDIA GPU for Data Science on your local PC or one bare-metal cloud server, let’s see how CodeReady Containers works.
Open Data Hub v0.5.1 release
Open Data Hub v0.5.1 was released February 16, 2020.
Release node: https://opendatahub.io/news/2020-02-16/odh-release-0.5.1-blog.html
Open Data Hub includes many tools that are essential to a comprehensive AI/ML end-to-end platform. This new release integrate some bug fixes that resolve issues when deploying on OpenShift Container Platform v4.3. JupyterHub deployment and Spark cluster resources have now a greater customization. Let’s try the Data science tools JupyterHub 3.0.7 on OpenShift 4.3.
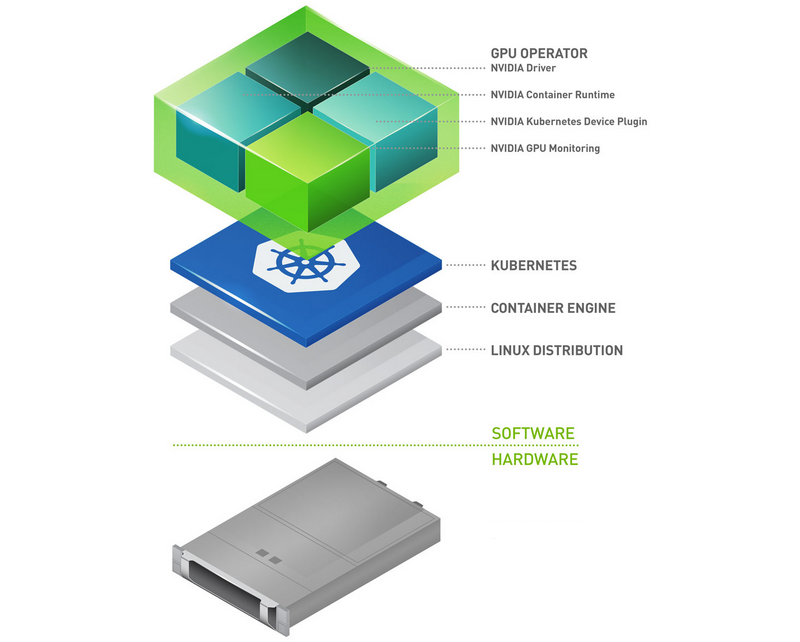
NVIDIA GPU Operator with OpenShift 4.3 on Red Hat OpenStack Platform 13
The NVIDIA GPU Operator has been available as a Beta since 2020, Jan 27, it’s a technical preview release: https://github.com/NVIDIA/gpu-operator/release
The GPU Operator manages NVIDIA GPU resources in an OpenShift cluster and automates tasks related to bootstrapping GPU nodes. Since the GPU is a special resource in the cluster, it requires a few components to be installed before application workloads can be deployed onto the GPU, these components include:
OPAE with Intel FPGA PAC with Arria 10 GX
OPAE is the Open Programmable Acceleration Engine, a software framework for managing and accessing programmable accelerators (FPGAs): https://01.org/opae
The OPAE SDK is open source and available in this git: https://github.com/OPAE/opae-sdk
How to enable NVIDIA T4 GPU with podman
We will enable GPU with Podman on a RHEL 8.1 system with a NVIDIA Tesla T4:

Take a RHEL 8.1 system:
[egallen@lab0 ~]$ cat /etc/redhat-release
Red Hat Enterprise Linux release 8.1 (Ootpa)
Enable sudo passwordless:
Machine Learning benchmarking with OpenStack and Kubernetes, Shanghai OpenInfra summit
I’ve done a talk “Machine Learning benchmarking with OpenStack and Kubernetes” at Open Infrastructure Summit Shanghai 2019, November 4.
Abstract
Deep Learning and Cloud Platforms are transforming the field of Machine Learning from theory to practice. However, implementation differences across frameworks and inference engines make the comparison of benchmark results difficult. SPEC and TPCC benchmarks are not accurate due to the complex interactions between implementation choices such as batch size, hyperparameters, or numerical precision. To address this complexity requires systematic benchmarking that is both representative of real-world use cases and valid across different software/hardware platforms.
Red Hat OpenStack Platform 15 standalone
If you need to deploy quickly a testing Red Hat Openstack Platform environment, you can use standalone deployment available since Red Hat OpenStack Platform 14.
OpenShift 4.2 on Red Hat OpenStack Platform 13 + GPU
Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform 4.2 introduces the general availability of full-stack automated deployments on OpenStack. With OpenShift 4.2, containers can be managed across multiple public and private clouds, including OpenStack. Red Hat and NVIDIA are working to provide the best platform for Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning workloads.
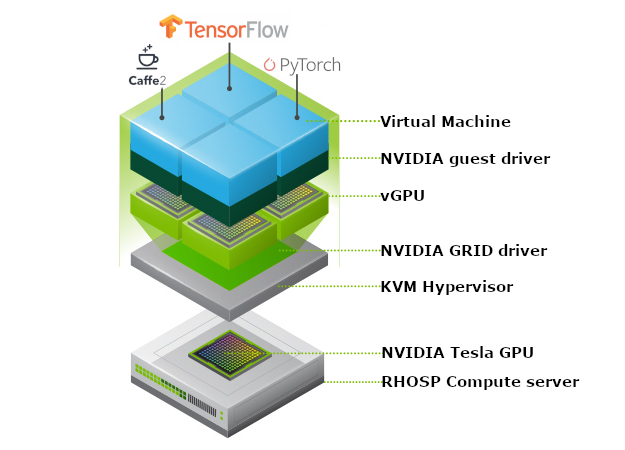
NVIDIA vGPU software and license server with RHOSP 15
We will describe the steps to try and download NVIDIA GRID software:
- Create a NVIDIA account
- Redeem your Product Activation Key (PAK)
- Download packages
- Prepare the VM and operating system of the license server based on RHEL 7.7
- Download the Virtual GPU license Manager for Linux
- Install the NVIDIA vGPU license Server
- Registering the License Server and Getting License Files
- Import the License Server file
- Launch an instance on a RHOSP 15 platform
- Instance status
- Compute node status
- Check the license status with CLI
- Check the license status in the dashboard
To enable NVIDIA GRID for Red Hat OpenStack Platform, you will need (example for RHOSP 8):\
How OpenStack enables Face Recognition with GPUs and FPGAs
I’ve done a talk “How OpenStack enables Face Recognition with GPUs and FPGAs” at OpenStack Day CERN 2019, May 27.
Abstract
Have you ever puzzled over the name of someone in a group picture? Now, thanks to OpenStack and TensorFlow, you don’t have to puzzle any more! In this talk, we will demonstrate a Face Recognition program that can identify that familiar face for you. We’ll also open the hood and show you how a Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) and Field-programmable gate array (FPGA) can be used with OpenStack to maximize the speed and accuracy of Face Recognition.
NVIDIA vGPU with Red Hat OpenStack Platform 14
Red Hat OpenStack Platform 14 is now generally available \o/
NVIDIA GRID capabilities are available as a technology preview to support NVIDIA Virtual GPU (vGPU). Multiple OpenStack instances virtual machines can have simultaneous, direct access to a single physical GPU. vGPU configuration is fully automated via Red Hat OpenStack Platform director.
NVIDIA Tesla GPU PCI passthrough with Red Hat OpenStack Platform 13
Red Hat OpenStack Platform provides two ways to use NVIDIA Tesla GPU accelerators with virtual instances:
- GPU PCI passthrough (only one physical GPU per instance)
- vGPU GRID (one physical GPU can be shared to multiple instances, Tech Preview OSP14)
This blog post is intended to show how to setup GPU PCI passthrough.
USB Passthrough with Red Hat OpenStack Platform 13
Some OpenStack users users would like to attach USB devices to OpenStack instances for security or legacy applications.
For example, a security application which run inside an OpenStack instance could require access to a Java card from an USB Gemalto eToken:
Libvirt snapshot delete cascade
When you want to delete/undefine a VM with libvirt, you must clean all the snapshots. You can make a bash loop or just the “--children” parameter: